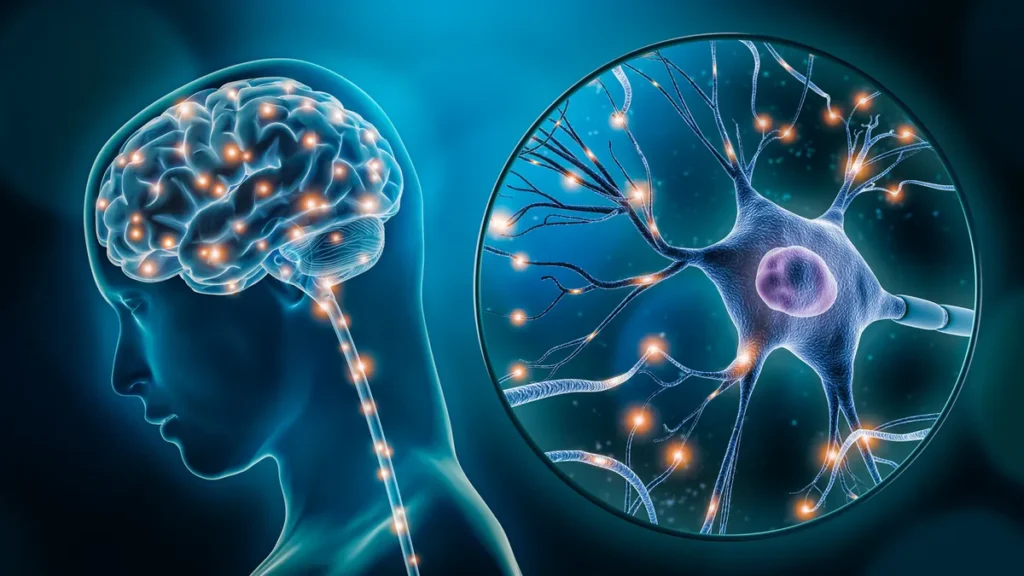
Psychedelics have specific actions, such as inducing structural and functional neural plasticity, that treat mental health conditions and impact diseases affecting the brain, like Alzheimer’s Disease.
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a brain disorder, typically occurring in seniors, that disrupts the communication between neurons and causes cell death. It is usually found in brain regions responsible for memory, learning and attention.
This interruption of signals is caused by a buildup of harmful proteins called neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid-beta, which cause inflammation in the brain.
Inflammation, AD, & Psychedelics
Neuroinflammation goes beyond being a pathological hallmark of Alzheimer’s. Every risk factor we know of — genetic and environmental — is associated with it . It’s a big deal, which is why it’s being researched as a way to prevent AD.
Classic psychedelics’ affinity for 5HT2A-R gives them unique anti-inflammatory properties that target brain tissue. Specifically, they help control amyloid precursor (APP) processing loops — which I discuss next — and balance out chronic microglial activation .
Microglia are like the brain’s janitor; they’re in charge of cleaning out cellular waste, dead cells, neurons that don’t communicate properly, and proteins implicated in neurodegenerative disorders. However — they do this by causing inflammation, the body’s way of fighting infection. When they’re causing ongoing inflammation, as they do for Alzheimer’s, healthy brain cells start to die. Keeping them under control saves brain cells.

Amyloid-Beta
Interestingly enough, LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide) shows extra benefits — it easily crosses the blood-brain barrier (BBB), something common NSAIDs fail to do .
All serotonergic psychedelics modulate amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing loops and have potent anti-inflammatory effects.
However, studies show chronic use of LSD also reduced cortical soluble amyloid-beta (Aβ) proteins 40 and 42; both are isoforms of APP, but Aβ42 is thought to be particularly toxic.
Amyloid-beta is what triggers Alzheimer’s progression and is a marker for the disease.
Neuroplasticity, Neurogenesis, & Psychedelics
Neurogenesis is the process of new brain neurons forming. Decreased neuron production is linked to psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders and can make cognitive deficits more pronounced.
Adult neurogenesis happens in two brain regions — the subgranular zone (SGZ) and the subventricular zone (SVZ) .
Neuroplasticity is summed up like this — “Plasticity refers to the ability of the nervous system to dynamically modulate its function in response to ongoing internal activities or external experiences. Plasticity is a normal and essential part of cognition, also an important means by which the brain can respond to damage.”
It can break down even further. There’s synaptic plasticity, which is how well transmissions cross the synapses, and structural plasticity, which is the synapses’ physical structure.
It’s possible that the synapses are the link between amyloid and pathologies and the cognitive symptoms of AD. Boosting neuroplasticity could help improve cognition in AD patients.

Dendritic Spines
Dendric spine loss strongly correlates to cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s and is yet another avenue researchers are looking at for treating this disease.
Psilocybin, the main compound in magic mushrooms, increases spine density and size, essentially remodeling their structure and making changes that last at least one month. This comes along with increased neurotransmission.
Synapses
Reduced neurons and synaptic structural changes, abnormalities, damage, loss, and dysfunctions happen in the early stages of Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases — often before any behavioral symptoms show .
Late-stage AD goes hand-in-hand with an enormous loss of neurons and synapses, which is when the damage becomes apparent .
An article says psilocybin’s “synaptic rewiring in the cortex is fast and enduring,” and other SPs show similar results .
One hypothesis for why the effects last so long is because of their ability to cause neurons in the pre-frontal cortex (PFC) to grow, leading to structural and functional neuroplasticity and restored synaptic connections. Many psychiatric disorders show the atrophy of these neurons .
Another study showed that LSD, psilocybin, DMT, and DOI do the following :
- Promote immediate early genes (IEGs) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expressions, among others that have to do with synaptic plasticity
- Increase long-term potentiation
- Cause synaptic and dendritic growth
- Stimulate 5-HT2A receptors on GABAergic interneurons
S1R Receptors
Here we have yet another target for AD treatment. There are two subtypes — sigma-1 and sigma-2.
Sigma 1 receptors (S1Rs) were considered a sub-type of opioid receptors, but now it’s accepted that they are not. Instead, they bind to many classes of psychotropic substances.
Sigma-1 receptors are mostly in the laminae of the cortex, olfactory bulb, hypothalamus, mesencephalon, and Purkinje cells — parts that are for higher-brain functions like memory and drug dependence.
These receptors do many helpful things in regard to AD and the brain, such as :
- Prevent amyloid-B-induced neurotoxicity
- Are neuroprotective
- Encourage neuroplasticity
- Mobilize synaptic receptors
- Increase neuroimmunomodulation
- Control neurogenesis
On the other hand, losing S1Rs speeds up neurodegeneration; recessive mutations are linked to some forms of dementia, and polymorphisms increase the risk of AD .
DMT & S1Rs
A 2021 study looked at N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) and PRE084 — both S1R agonists — and how they affected the brain.
DMT bound to S1R moderately and had a high affinity for 5-HT receptors. It significantly reduced astrogliosis — changes that happen to astrocytes due to CNS injury or disease. These cells have many roles — they provide nutrients, recycle neurotransmitters, and do other jobs that help keep things balanced.
DMT is also anti-inflammatory and increases dopaminergic neurotransmission, along with synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis, but has other potential regarding memories. Anecdotal reports say ayahuasca helps retrieve memories; using DMT and MAOIs might activate memory-related parts of the brain and have anti-amnesic effects .
Psychedelics, Depression, & AD
Depression and Alzheimer’s are a little too comfortable with each other — their relationship is bidirectional, meaning depression is a risk factor for AD, and AD is a risk factor for depression.
In these cases, depression might be due to severe neurodegeneration and not actual clinical depression. Several factors can cause depression in AD patients — tau pathology, amyloid accumulation, inflammation, and faulty neurotransmitter signaling .
Other brain changes overlap, showing up in AD and late-life depression, like reduced hippocampal volume and neuronal death in areas related to emotions and cognition.
Could this be where psychedelics step in and save the day? Possibly — they are shown to be quite effective for depression. There could be multiple ways this could go; psychedelics would treat depression brought on by AD, help prevent the disease in the first place, or both.