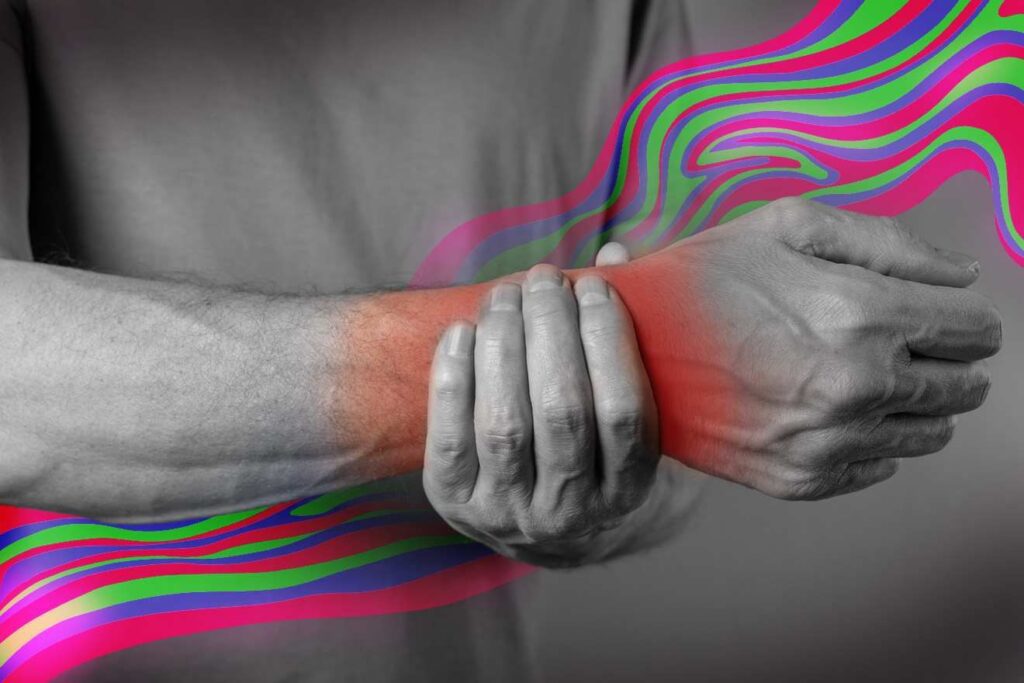
Many people worldwide use alternative medicine like marijuana to help ease their pain. What about using psychedelics for inflammation? Their hallucinogenic properties can take users to another planet mentally, but they may also have several therapeutic benefits.
What Is Inflammation?
The human body has a built-in network that responds to pain and physical trauma. When bacteria, viruses, or toxic chemicals come into contact with the body, the immune system springs into action. The same happens when experiencing injuries.
The body produces inflammatory cells, sending them to the affected site to trap bacteria and toxins and start the healing process. Inflammation occurs as a result, causing swelling, pain, redness, heat, or bruising.
The immune system also sends out cytokines, which help produce more inflammatory cells. While the healing process takes place, the body may have other reactions. There might be a reduced sense of smell, difficulty breathing, or fever and exhaustion.
Using psychedelics for inflammation could work by targeting prostaglandins and reducing or slowing down their production.

More studies are revealing the multifaceted applications of naturally-occurring psychoactive compounds. Some of these substances have helped people recover from drugs, heal from trauma, and experience mental and physical rejuvenation.
How can psychedelics act as anti-inflammatories? We explore the fascinating healing science behind them and how they might also improve neuroplasticity in the brain. Fasten those seatbelts as we take a joyride through the human body’s remarkable biological networks.
Psychedelics Contain Anti-Inflammatory Properties?
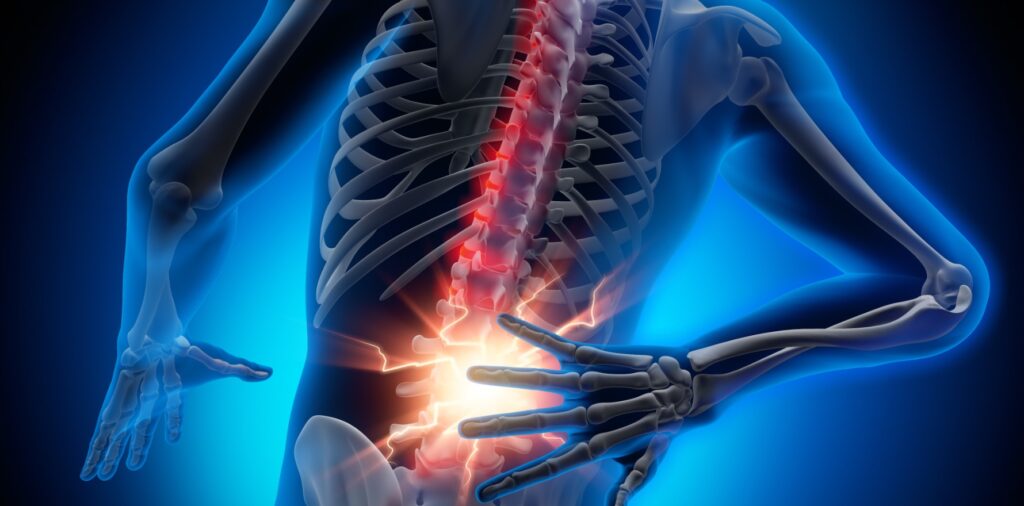
Specific receptors in the brain contribute to healing and pain relief. 5-hydroxytryptamine-2A (5-HT2a) is one that, when activated, have anti-inflammatory effects.
It can work as a central nervous system neurotransmitter and modulate endocrine, cardiovascular, and developmental functions. It can also mediate working memory, cognitive behaviors, and vasoconstriction.
The receptor is in many tissue types like muscle, immune, endocrine, and endothelial. Serotonin helps stimulate it to reduce pain and diminish some physical symptoms. A study examining psilocybin effects on 5-HT2a showed positive results for the psychedelic substance.
The research indicated that the occupancy of the receptor and plasma psilocin concentration means psychedelics help inflammation. It also acknowledged that microdosing have positive mental benefits like improved mood and enhanced creativity.
Other therapeutic applications of psychedelics include treating:
- Chronic pain
- Mood disorders
- Substance abuse
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
- Cluster headaches
- Stress and anxiety
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Depression
- Psychological distress
Another study on the anti-inflammatory effects of psychedelics , psilocybin showed that the compound help inhibit pro-inflammatory mediators. It could reduce pain, treat pathological sensitivity, and halt the production and dispersion of cytokines.
What Is Neuroplasticity?
Psychedelics help inflammation by improving the brain’s ability to reorganize or form synaptic connections and neural networks. This is known as neuroplasticity, where the nervous system adapts and changes to promote cognitive ability and re-wire specific pathways.
This natural process begins at birth and doesn’t stop functioning until death. There are two primary types: structural and functional. The former involves changing the strength of neuron or synapse connections.
Functional neuroplasticity makes permanent synapse changes and contributes to development, cognition, and learning.
There are several benefits of neuroplasticity, including:
- Learning and retaining knowledge and improving memory
- Boosting cognitive capability and “brain fitness”
- Strengthening and healing lost or damaged brain function
- Recovering from brain trauma, injuries, and strokes
How Psychedelics Might Help Increase Neuroplasticity
To understand how psychedelics could help inflammation, let’s explore how they might improve neuroplasticity.
Several studies indicate that psychedelics like psilocybin, LSD, and ayahuasca have anxiolytic, cognitive, antidepressant, and anti-addictive benefits. A systematic review of neuroplasticity suggests that each hallucinogenic substance acts differently.
The study’s outcomes showed that psychedelics could promote molecular and cellular neuroplasticity after one or more administered doses. They work similarly to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), potentially easing depression symptoms.
In addition, the study presented evidence of psychedelics acting on 5-HT2a receptors, which results in anti-inflammatory effects. It also acknowledged that certain hallucinogenic substances enhance cognitive and social skills, creativity, empathy, and general well-being.