1. Treatment-Resistant Depression (TRD):
This is perhaps the most well-known and researched benefit of ketamine. TRD refers to depression that hasn’t responded to traditional antidepressant medications (like SSRIs or SNRIs) after multiple trials.
How it Works
Traditional antidepressants primarily target serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. Ketamine, on the other hand, primarily affects the NMDA receptor in the brain. This receptor is involved in glutamate signaling, which is crucial for brain plasticity (the brain’s ability to change and adapt). By modulating NMDA receptors, ketamine is thought to increase the release of glutamate, which then triggers a cascade of events that ultimately lead to the formation of new neural connections and improved mood. Essentially, it helps “reset” or “reboot” certain brain circuits involved in depression.
Important Notes:
- The effects of ketamine for depression are often rapid (within hours or days), but they are usually not permanent. Maintenance treatments are often needed.
- Ketamine is not a “cure” for depression. It’s a treatment that can provide relief from symptoms.
- It’s crucial to be under the care of a psychiatrist or mental health professional experienced in ketamine therapy.
2. Suicidal Ideation:

Related to its effectiveness in TRD, ketamine has also demonstrated the ability to rapidly reduce suicidal thoughts in individuals experiencing acute suicidal crises.
How it Works
The rapid antidepressant effects of ketamine quickly alleviate the hopelessness and despair that often drive suicidal ideation. By improving mood and cognitive function, it can provide a window of opportunity for individuals to engage in therapy and develop coping mechanisms.
Important Notes:
- Ketamine is not a substitute for comprehensive mental health care.
- It’s crucial to have a safety plan in place and ongoing support after ketamine treatment.
- The reduction in suicidal ideation is often temporary, requiring continued treatment and monitoring.
3. Chronic Pain Management:

Ketamine can be used to manage certain types of chronic pain, particularly neuropathic pain (pain caused by nerve damage). This includes conditions like complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), fibromyalgia, and phantom limb pain.
How it Works
Ketamine’s mechanism of action for pain relief is complex and not fully understood. It’s believed to involve:
NMDA Receptor Antagonism: Blocking NMDA receptors can reduce the transmission of pain signals in the central nervous system.
Modulation of the Opioid System: Ketamine can interact with opioid receptors, potentially enhancing the effects of opioid pain medications or reducing the need for them.
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Ketamine have anti-inflammatory properties that contribute to pain relief.
Central Sensitization: Ketamine can help reverse central sensitization, a condition where the central nervous system becomes hypersensitive to pain signals.
Important Note:
- Ketamine is typically used for chronic pain when other treatments have failed.
- It’s often administered in low doses via infusion.
- Long-term use of ketamine for pain can have side effects, so careful monitoring is essential.
4. Anesthesia and Sedation:
Ketamine has been used as an anesthetic agent for decades, particularly in emergency medicine, pediatric anesthesia, and veterinary medicine. It can provide both anesthesia (loss of sensation) and analgesia (pain relief).
How it Works
Ketamine dissociates the brain from sensory input, creating a trance-like state. It’s unique compared to other anesthetics in that it typically doesn’t significantly suppress breathing or blood pressure at lower doses, making it useful in situations where respiratory compromise is a concern.
Important Notes:
- Ketamine anesthesia is typically used for short procedures or in situations where other anesthetics are not suitable.
- It can cause hallucinations and emergence reactions (confusion and agitation) .
- It’s often combined with other medications to reduce these side effects.
5. Bronchospasm:
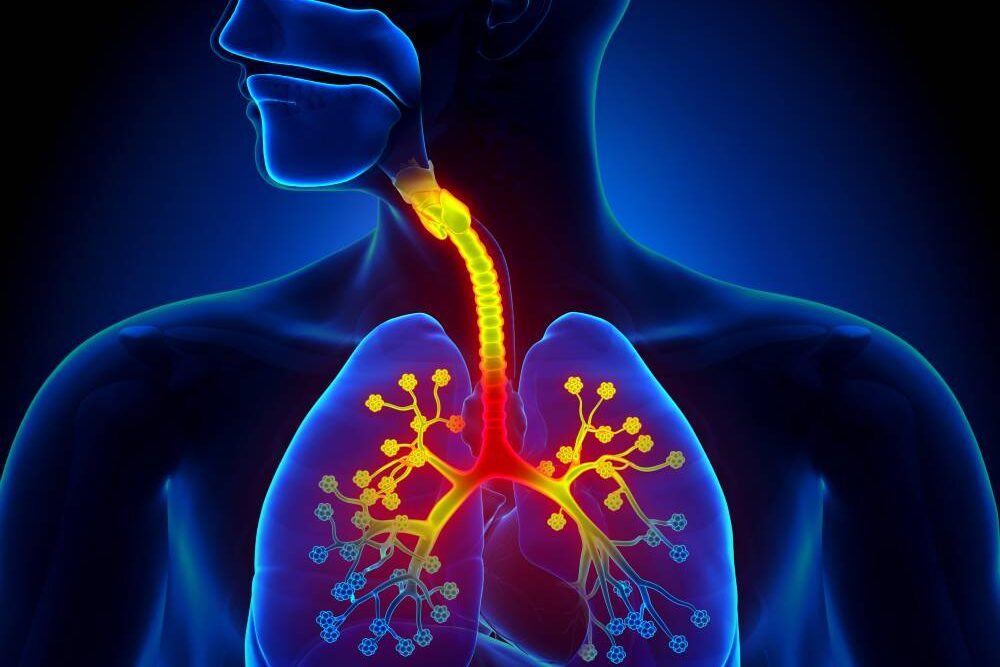
Ketamine can be used to treat bronchospasm (constriction of the airways in the lungs) in certain situations, particularly in patients with asthma or other respiratory conditions.
How it Works
Ketamine has bronchodilating properties, meaning it can help relax the muscles in the airways, making it easier to breathe.
Important Notes: This is not a first-line treatment for bronchospasm, but it can be helpful when other medications are not effective or are contraindicated.
Conclusion

In conclusion, ketamine offers significant therapeutic potential for conditions like treatment-resistant depression, suicidal ideation, and chronic pain, while also serving as a valuable anesthetic agent. However, its powerful effects necessitate cautious and closely monitored use under the guidance of qualified medical professionals . It’s a tool with considerable benefits, but one that demands respect and responsible application.