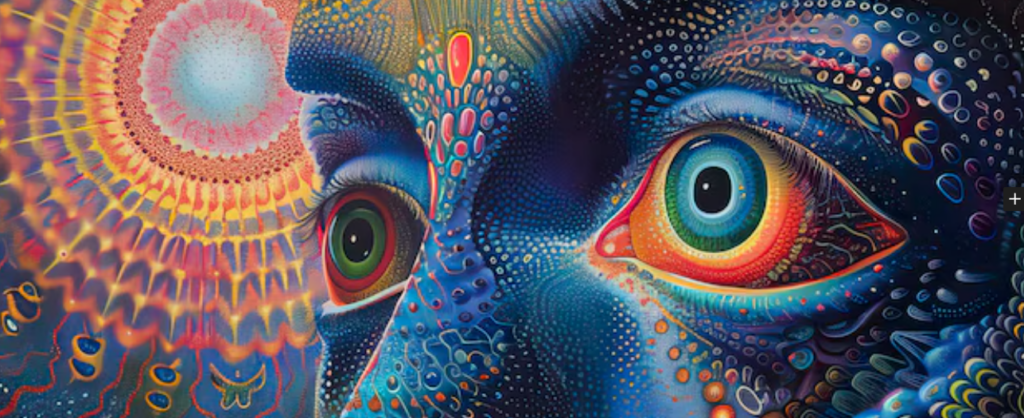
Lysergic acid diethylamide, more commonly known as LSD, has intrigued both scientists and the public since its discovery in the 20th century. This powerful psychedelic has been the subject of extensive research and debate around its effects on the human mind and consciousness. As we delve into the world of LSD, we will uncover what this substance is, how it works in the brain, the multifaceted nature of consciousness itself, and how the two intertwine to influence the evolution of human consciousness.
What is LSD?
LSD is a potent hallucinogenic drug that is derived from ergot, a fungus that grows on rye and other grains. Discovered in 1938 by Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann, LSD was initially researched for its potential in treating various mental health disorders. By the 1960s, it had gained popularity in counterculture movements and was commonly associated with the exploration of spirituality and consciousness.
Chemical Structure: LSD is part of a larger family of compounds known as ergolines. Its structure closely mimics serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in mood regulation and perception.
Administration: LSD is usually consumed in small doses, often as a liquid on blotter paper, in capsules, or as a liquid solution. A single dose can lead to profound changes in perception, mood, and cognitive functioning.

How LSD Works
LSD primarily exerts its effects by interacting with serotonin receptors in the brain, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor. This interaction increases communication within certain neural networks and decreases the influence of the default mode network, which is associated with self-referential thought and the ego.
Mechanism of Action
1. Receptor Binding: LSD binds to serotonin receptors, altering the release of neurotransmitters and enhancing synaptic plasticity.
2. Neural Connectivity: Studies using brain imaging have shown that LSD increases connectivity between different brain regions, resulting in a novel pattern of neural activity that can sometimes lead to synesthesia—where one sense is perceived through another, such as “seeing” sounds.
3. Consciousness Alteration: The result is a profound change in perception, potentially facilitating experiences of unity, interconnectedness, and transcendence that some users describe as spiritual or cosmic in nature.

What is Consciousness?
Consciousness is one of the most complex and debated topics in philosophy, neuroscience, and psychology. It can be broadly defined as the state of being aware of and able to think about one’s own existence, thoughts, and environment. While there are many theories regarding the nature of consciousness, several key aspects are generally agreed upon:
Awareness: The ability to recognize and respond to internal and external stimuli.
Subjective Experience: Consciousness encompasses personal experiences and feelings, often described as “qualia.”
Self-Reflection: This includes the capacity for introspection, where individuals can think about their thoughts and emotions.
LSD and the Evolution of Consciousness

hh
The relationship between LSD and consciousness has been a topic of exploration for researchers and theorists alike. Proponents of psychedelic research argue that psychedelics like LSD can offer unique insights into the nature of consciousness.
Transformative Experiences
Expanded Perspectives: Users often report experiences that challenge traditional perceptions of reality. Such experiences can engender a sense of connectedness with others and the universe, suggesting an evolutionary step in human consciousness.
Creativity and Innovation: Artists, writers, and scientists have historically utilized LSD to unlock creative barriers, leading to breakthroughs in their respective fields. This demonstrates how altered states of consciousness can foster innovative thinking.
Therapeutic Applications: Emerging research indicates that LSD and other psychedelics may have therapeutic benefits for mental health conditions such as PTSD, depression, and anxiety. By altering one’s consciousness, these substances may provide new frameworks for understanding and processing emotional trauma.
Conclusion
LSD plays a multifaceted role in the exploration and understanding of consciousness. By serving as a catalyst for expanded awareness and creative thought, it invites us to reconsider what it means to be conscious. As research into psychedelics continues to grow, we may find new avenues for therapeutic applications and insights into the complexities of human consciousness itself. The journey of LSD from the laboratory to the minds of individuals reflects a deeper quest for understanding, evolution, and potentially, higher states of being. In a world increasingly open to discussions on the human experience, perhaps LSD will play a pivotal role in the ongoing evolution of consciousness.