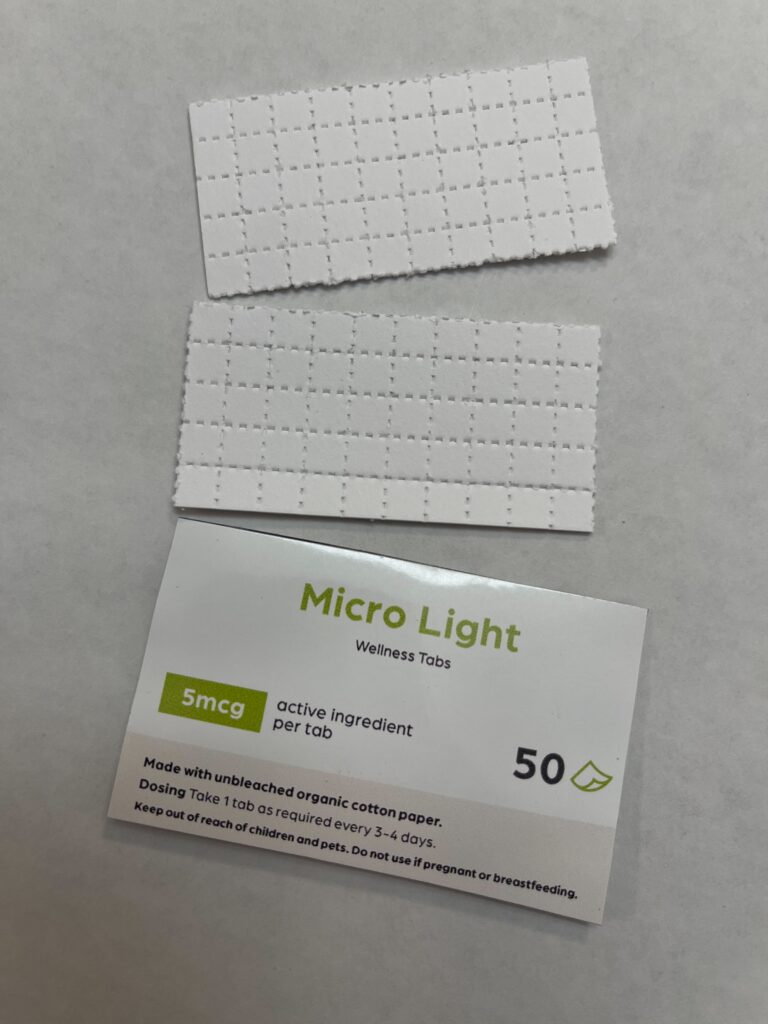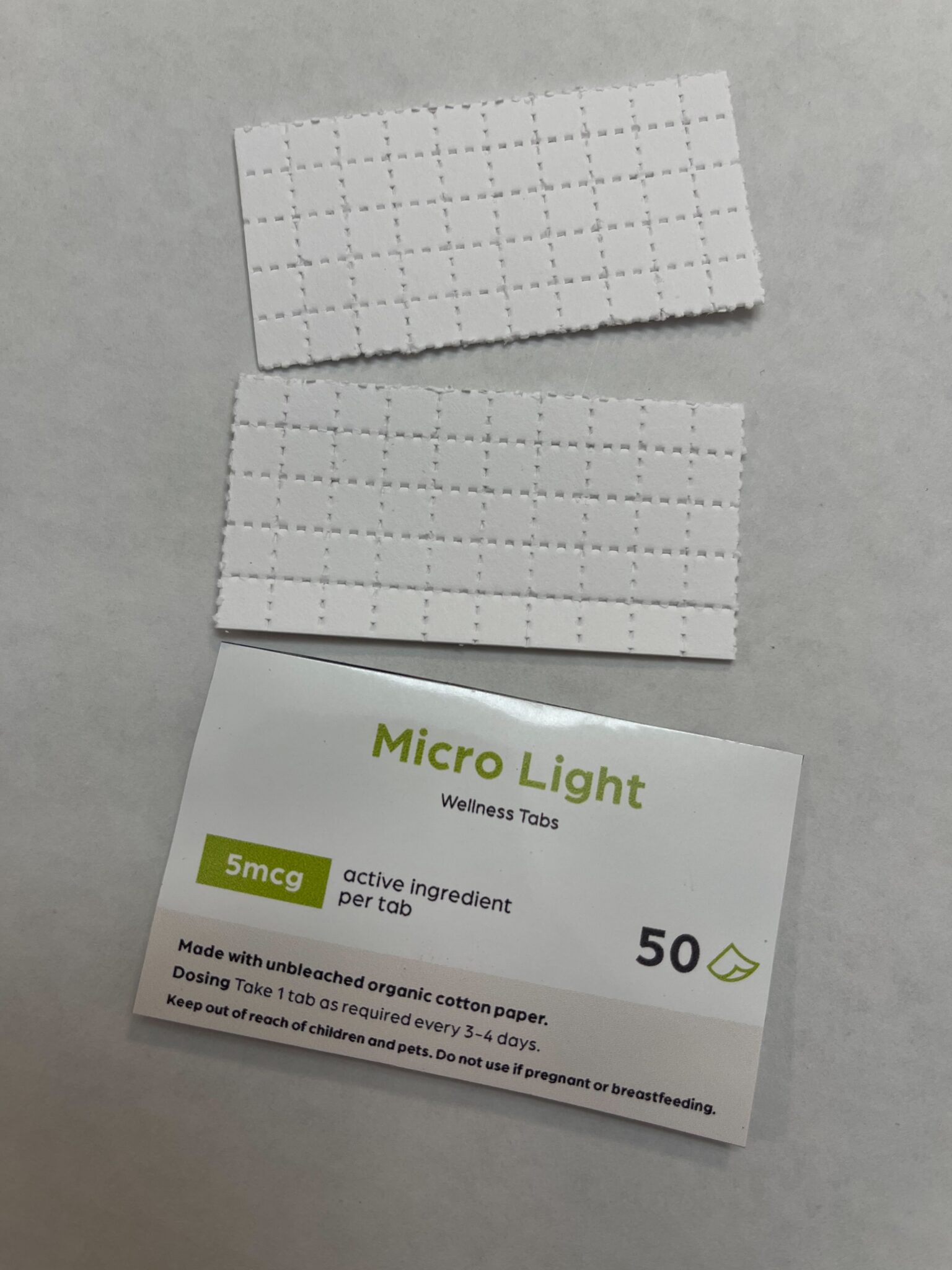
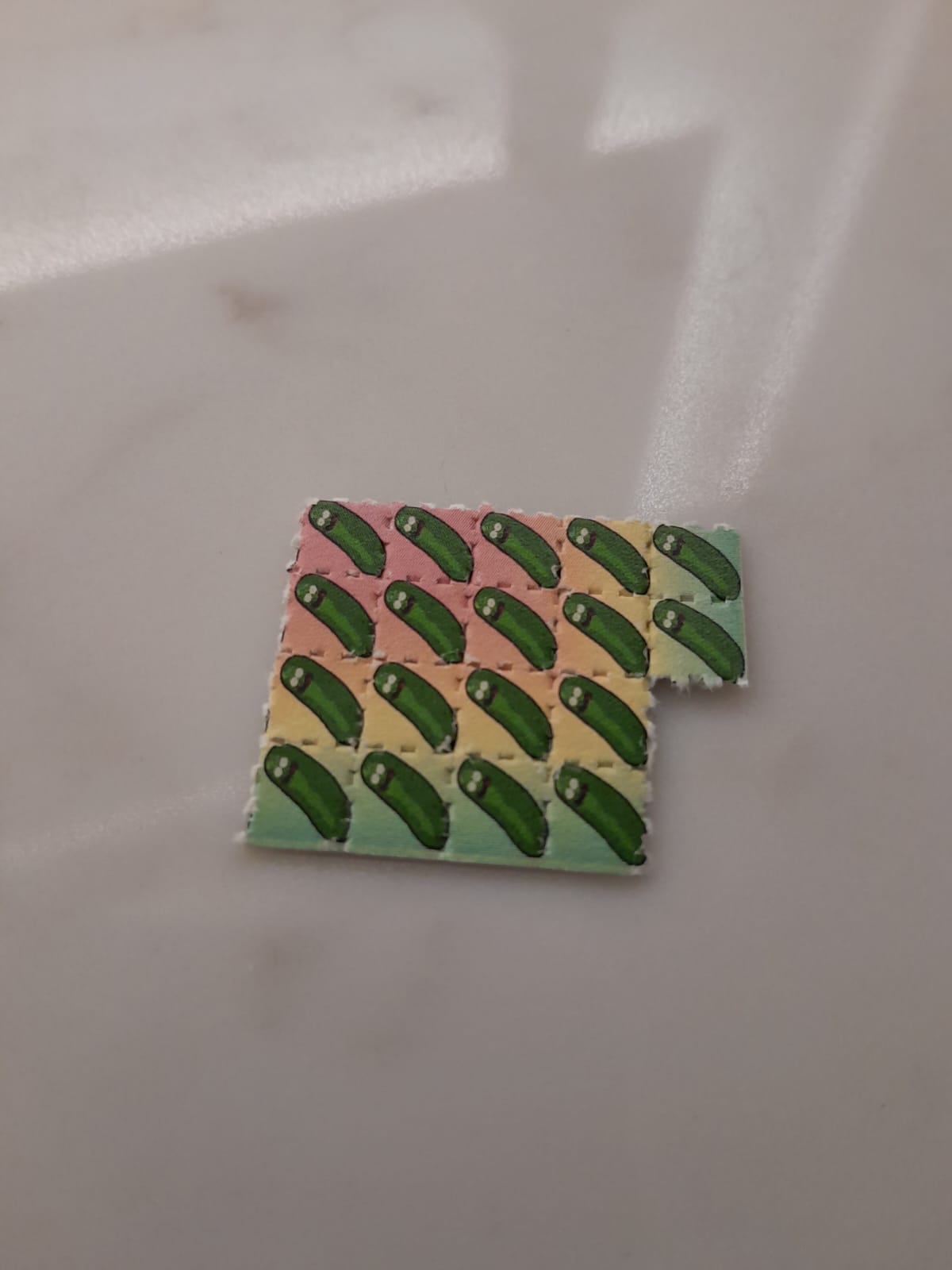
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) has long been an enigma, often associated with counterculture movements and recreational use. However, a growing body of research suggests that LSD have potential applications in enhancing learning and cognitive functioning. As we delve into the complexities of this psychedelic compound, we explore its definition, historical context, and uses as an innovative learning tool.
Understanding LSD

What is LSD?
LSD is a potent hallucinogenic that alters perceptions, thoughts, and feelings. First synthesized in 1938 by Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann, it gained popularity in the 1960s for its potential to expand consciousness.
Mechanism of Action
LSD primarily affects serotonin receptors in the brain, particularly the 5-HT2A variant. This interaction can lead to heightened sensory perception, altered emotional states, and profound introspective experiences. Some studies have suggested that this enhanced connectivity in the brain can facilitate new approaches to learning and problem-solving.

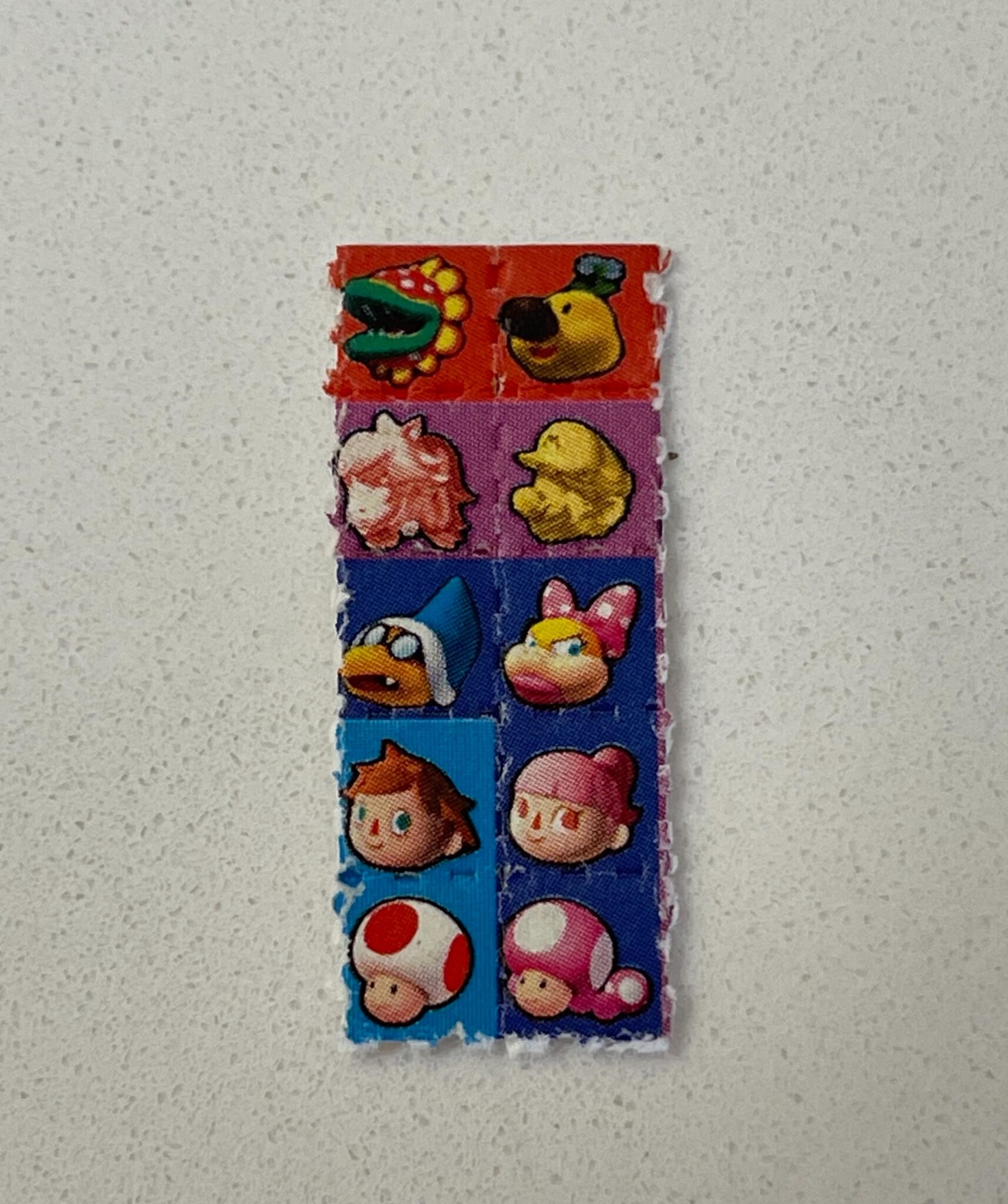
Challenging Traditional Learning Approaches
Most traditional learning methods often rely on rote memorization and standardized testing. These systems can stifle creativity and discourage free-thinking. LSD’s psychoactive properties present a unique opportunity to break this paradigm by promoting a more open-minded, experiential learning environment.
Reducing Psychological Barriers
Psychological factors, such as anxiety and fear of failure, can significantly hinder learning processes. LSD has been reported to reduce these barriers by fostering a sense of connectedness and openness. Users often describe profound experiences that allow them to approach problems from a new perspective, promoting resilience and adaptability in the learning process.

How to Use LSD as a Learning Tool
1. Set and Setting
To harness the positive aspects of LSD as a learning tool, it is essential to consider two key factors: the mindset (set) and the environment (setting). A positive and intention-driven mindset can lead to more fruitful learning experiences.
2. Reflection and Integration
After the experience, reflection is crucial for consolidating learning. Journaling or discussing insights with peers can help process newfound knowledge and experiences, thereby solidifying it into actionable understanding. Integration involves finding practical applications for these insights in daily life or academic pursuits.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, LSD presents a unique set of properties that revolutionize the way we approach learning. By breaking traditional educational paradigms, reducing psychological barriers, and harnessing its psychoactive benefits in a structured way, learners may find new pathways to insight and knowledge. This exploration, however, must be approached with caution, ethical considerations, and a commitment to responsible use. As society continues to test the boundaries of education through innovative methods, the role of LSD as a learning tool warrants serious and ongoing discussion.