Knowledge of the miraculous health benefits of mushrooms is surely seeping into the mainstream. And two mushrooms leading this charge are lion’s mane mushrooms and psilocybin-containing ‘magic’ mushrooms.
These two shrooms share a remarkable ability: they can increase the growth of new brain cells, potentially offering a way to help people change the neural networks in their brain, which can in turn allow people to alter habits and ingrained behavior’s.
The theory that combining lion’s mane and psilocybin may offer even more profound nerve regenerating effects, making it a potential treatment for conditions such as peripheral neuropathy and traumatic brain injury, among others.
To understand why you might want to use both lion’s mane and psilocybin, it’s important to understand the process of neurogenesis.
Neurogenesis explained
The powerful effects of both lion’s mane and psilocybin mushrooms on the brain can be partly explained by the fact that both enhance neurogenesis.
Neurogenesis is the process by which new neurons (nerve cells) are generated from neural stem cells and progenitor cells in the brain. It involves the formation, differentiation, and integration of these new neurons into existing neural circuits.
In very simplified terms, both substances can effectively help regenerate and ‘rewire’ the brain.
Neurogenesis occurs primarily in specific regions of the brain, such as the hippocampus, which plays a crucial role in learning, memory, and emotion.
Throughout life, the brain retains the ability to produce new neurons in certain regions, although the rate of neurogenesis tends to decrease with age. This process is essential for various cognitive functions, adaptability, and brain plasticity.
Neurogenesis is a complex and dynamic process that contributes to the brain’s ability to adapt, learn, and recover from injury. By influencing this process, both lion’s mane and psilocybin offer a unique way to affect brain function.
What is lion’s mane?
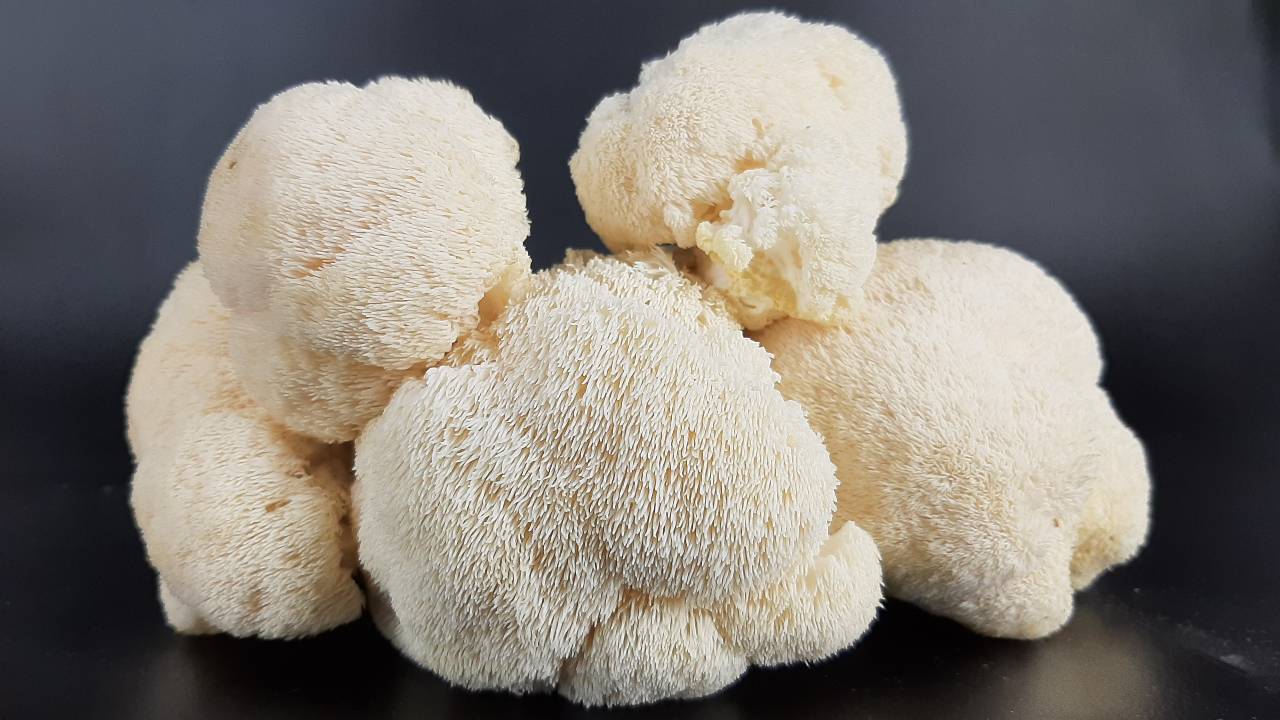

Lion’s Mane (Hericium erinaceus) is a type of mushroom that is recognised for its distinctive appearance, which resembles the mane of a lion, and valued not only for its culinary uses but also for its health benefits.
In traditional medicine, lion’s mane has been used for centuries in Asia, particularly in Chinese and Japanese herbal practices.
It has gained attention in the west in recent years due to its potential neurological and cognitive benefits.
How does lion’s mane work?
One recent study found that a compound in lion’s mane called Hericene A is responsible for the nerve generating effects of lion’s mane.
Hericene A works promoting neuron projections, extending and connecting to other neurons, ultimately increasing the size of growth cones, which play a crucial role in brain cells sensing their environment and establishing new connections with other neurons in the brain.
What is psilocybin?
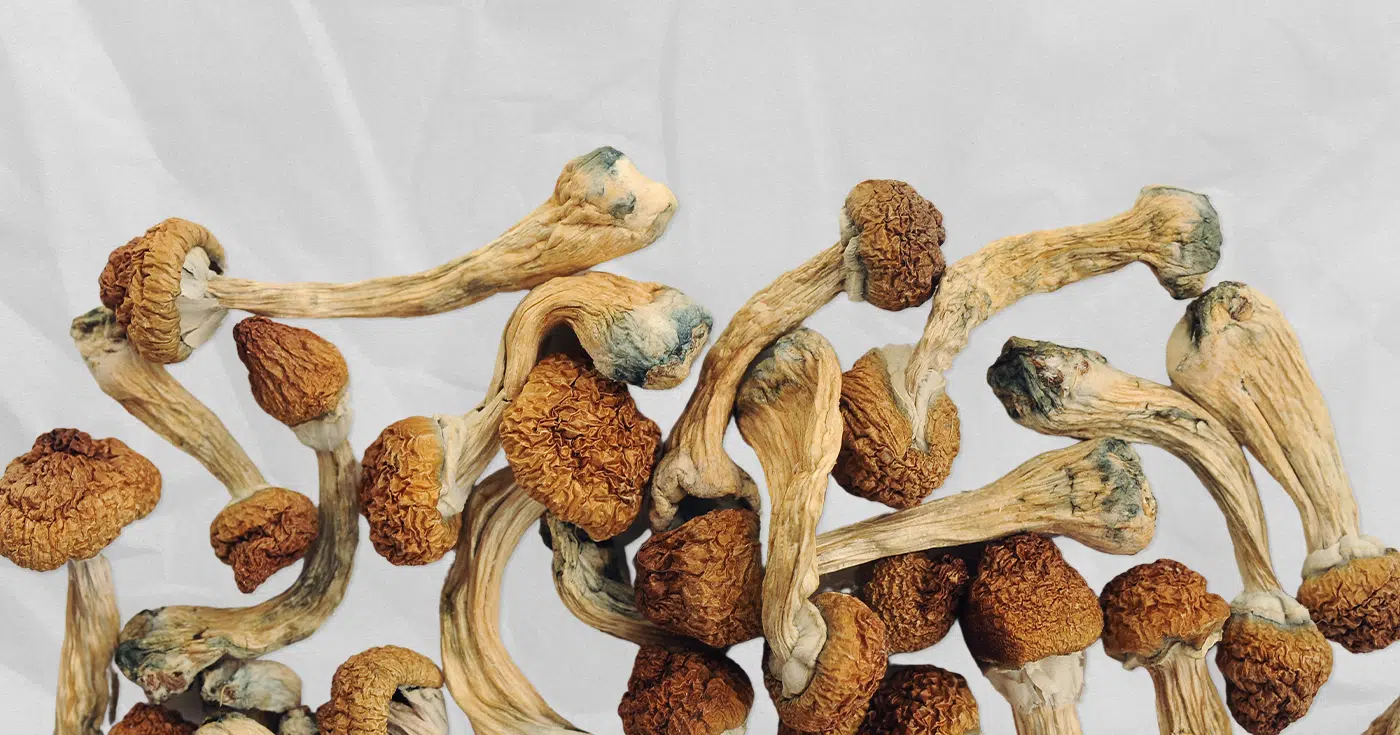

Psilocybin is a naturally occurring psychedelic compound found in certain species of mushrooms, often referred to as “magic mushrooms”.
When ingested, psilocybin is metabolised by the body into psilocin, which is the active form responsible for the hallucinogenic and psychoactive effects associated with consuming these mushrooms.
Psilocybin-containing mushrooms have been used for centuries in various cultures for their potential spiritual, therapeutic, and recreational effects. They have been traditionally used in religious and shamanic rituals for altered states of consciousness and insights.
Studies suggest that psilocybin-assisted therapy could have benefits for various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and substance use disorders.
How does psilocybin work?
Research into the potential therapeutic uses of psilocybin has been growing in recent years.
Psilocybin primarily affects the brain by binding to serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in mood regulation, cognition, and other functions. Some research suggests that the activation of 5-HT2A receptors may be involved in the stimulation of neurogenesis.
Psilocybin also promotes the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that plays a crucial role in promoting the survival, growth, and maintenance of neurons.
Some research suggests that psilocybin may have anti-inflammatory properties, and it may influence glutamate neurotransmission, which is involved in various neural processes, including neuroplasticity and neurogenesis.
What is microdosing?

Microdosing refers to the practice of taking very small, sub-perceptual doses of psychedelic substances, such as LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide) or psilocybin-containing mushrooms, with the intention of experiencing subtle cognitive, emotional, or creative effects without inducing a full-blown psychedelic experience or “trip.”
Microdosing typically involves taking a fraction of a standard recreational dose, often one-tenth or less, on a regular schedule. The goal is to achieve a “microdose” that is below the threshold for producing hallucinations or major perceptual changes but is still thought to influence mood, focus, energy, and other cognitive functions.
Advocates of microdosing suggest that it may lead to improved creativity, productivity, mood, and overall well-being. Some users report enhanced problem-solving abilities, increased sociability, and reduced symptoms of anxiety or depression.
Benefits of combining lion’s mane and psilocybin
Here are some potential benefits that have been proposed of combining lion’s mane and psilocybin, based on current knowledge and anecdotal reports:
- Cognitive enhancement
Lion’s mane and psilocybin have been shown to have neurotrophic properties, promoting the growth and health of neurons. Combining them amplify the cognitive benefits, leading to improved focus, memory, and overall cognitive function.
- Neuroplasticity
Again, both substances are known to promote neuroplasticity, which is the brain’s ability to reorganise and form new neural connections. Combining them could enhance the brain’s adaptability and capacity for learning and change.
- Mood regulation
Psilocybin and lion’s mane have been studied for their potential to alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders. Combining them could provide a more effective approach to emotional well-being.
- Creativity
Some individuals report heightened creativity and increased access to insights during microdosing, while lion’s Mane’s reputation for fostering creative thinking could potentially enhance this aspect of the experience.
- Neuroprotection
Both Lion’s Mane and psilocybin have been investigated for their potential neuroprotective properties, which could collectively contribute to maintaining brain health and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative conditions.
- Synergistic effects
The combination of these two substances could lead to synergistic effects, where their individual benefits are enhanced when used together, potentially leading to a more profound overall impact.